How to Plant Peonies From Seed
Acquiring and Preparing Peony Seeds
How to plant peonies from seed – Successfully growing peonies from seed requires careful attention to seed acquisition and preparation. This involves selecting high-quality seeds, cleaning them properly, and undergoing a process called stratification to break dormancy and improve germination rates.
Peony Seed Sources and Initial Cleaning
Peony seeds can be obtained from several sources. Online retailers offer a wide variety of peony cultivars, although seed viability can vary. Local nurseries may sell seeds or allow you to collect seeds from their mature plants, providing a more reliable source. Alternatively, if you already have established peony plants, collecting seeds yourself can be a rewarding experience. Once obtained, it’s crucial to clean the seeds.
Gently remove any excess pulp or debris clinging to the seeds. This helps prevent fungal growth and improves the chances of successful germination.
Stratifying Peony Seeds
Peony seeds require a period of cold stratification to mimic the natural conditions they experience over winter. This process breaks dormancy and significantly increases the germination rate. The following table Artikels the steps involved:
| Step | Action | Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mix peony seeds with a moist medium (e.g., vermiculite, peat moss) | N/A | Ensure the medium is damp, not soggy. |
| 2 | Place the mixture in a sealed container or zip-top bag. | N/A | Airtight container prevents moisture loss. |
| 3 | Refrigerate the container at 35-40°F (2-4°C) | 8-12 weeks | This simulates winter conditions. |
| 4 | Check moisture level periodically, adding a little water if needed. | Throughout stratification | Avoid letting the medium dry out completely. |
Sowing Peony Seeds: Methods and Timing: How To Plant Peonies From Seed
Choosing the right sowing method and timing is essential for successful peony seed germination. Direct sowing outdoors and starting seeds indoors in containers are the two primary approaches. The ideal timing depends heavily on your climate and specific peony variety.
Sowing Methods and Timing
Direct sowing outdoors is suitable in regions with mild winters, allowing seeds to experience natural stratification. Sow seeds in autumn after the first frost, ensuring the soil is well-drained. Starting seeds indoors in containers provides more control over the environment, particularly useful in colder climates. Start seeds indoors 8-12 weeks before the last expected frost, using a seed-starting mix and providing ample light.
Soil Requirements for Peony Seed Germination, How to plant peonies from seed
Peony seeds thrive in well-drained soil that is slightly acidic to neutral (pH 6.0-7.0). Heavy clay soils should be amended with organic matter (compost or peat moss) to improve drainage and aeration. Sandy soils may require the addition of organic matter to retain moisture. Proper drainage is crucial to prevent root rot, a common problem for peony seedlings.
Seedling Care and Germination
Once sown, maintaining the right environmental conditions and providing adequate care are vital for successful germination and seedling development. This includes careful monitoring of temperature, humidity, light, and watering.
Environmental Conditions and Watering

Source: squarespace-cdn.com
Peony seedlings germinate best in temperatures between 65-75°F (18-24°C). Maintain consistently moist but not waterlogged soil. Overwatering can lead to fungal diseases, while underwatering can stunt growth. Provide bright, indirect light; direct sunlight can scorch delicate seedlings.
Protecting Seedlings from Pests and Diseases
Young peony seedlings are susceptible to various pests and diseases. Prevention is key. Regularly inspect seedlings for signs of infestation or disease. Prompt action can save your plants.
- Common Pests: Aphids, spider mites, slugs, snails
- Common Diseases: Damping-off (fungal disease), Botrytis blight (fungal disease), root rot
- Preventative Measures: Use well-drained soil, avoid overhead watering, provide good air circulation, consider using organic pest control methods (e.g., insecticidal soap, neem oil).
Transplanting Peony Seedlings
Transplanting peony seedlings from containers to the garden or larger pots requires careful handling to minimize stress on the delicate roots. The optimal timing and size depend on the seedling’s growth stage and environmental conditions.
Transplanting Process and Timing
Transplant seedlings when they have developed several true leaves (usually 2-3 inches tall). Gently remove seedlings from their containers, ensuring not to damage the roots. Plant them in a prepared location with well-drained soil. The best time to transplant is in spring or autumn, avoiding periods of extreme heat or cold. Space seedlings according to the mature size of the peony variety.
Transplanting Schedule
A suitable schedule might involve starting seeds indoors in early spring, transplanting them into larger containers in late spring, and finally transplanting them into the garden in autumn or the following spring, depending on the climate.
Peony Seedling Aftercare and Growth
After transplanting, continued care is crucial for the healthy growth and development of peony seedlings. This involves regular watering, fertilizing, and mulching, as well as monitoring for any potential problems.
Post-Transplant Care
Water regularly, especially during dry periods. Apply a balanced, slow-release fertilizer in spring to promote healthy growth. Apply a layer of mulch (e.g., shredded bark, compost) around the base of the plants to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Common challenges include fungal diseases (root rot, botrytis blight), pest infestations (aphids, spider mites), and nutrient deficiencies. Proper soil preparation, appropriate watering, and preventative measures can help mitigate these issues. If problems arise, consult a gardening resource or local expert for guidance.
Peony Seedling Growth Stages
A visual representation would show the seedling emerging from the soil, developing its first true leaves, growing taller and producing more foliage, and finally developing buds and flowering, potentially taking several years to reach maturity depending on the variety.
Planting peonies from seed requires patience, as germination can be slow. The process involves careful seed preparation and consistent moisture. For a similar but faster-blooming option, you might consider researching techniques for how to plant chrysanthemum seeds , which often germinate more readily. Returning to peonies, remember to provide ample sunlight and well-drained soil for optimal growth.
Factors Affecting Peony Seed Germination and Growth
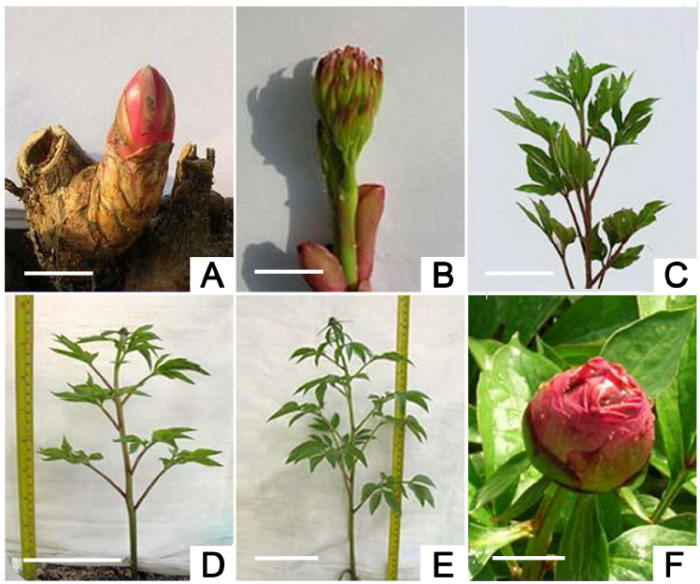
Source: researchgate.net
Several factors significantly influence the germination rate and overall growth of peony seedlings. These include inherent varietal differences, environmental conditions, and soil nutrient levels.
Germination Rates and Varietal Differences
Germination rates vary among different peony varieties. Some varieties are known for higher germination rates from seed than others. Herbaceous peonies, for instance, often have higher germination rates than tree peonies.
Environmental Factors and Growth Rate
Temperature and light intensity directly impact growth rate. Optimal temperatures promote faster growth, while insufficient light can lead to leggy growth. Consistent, moderate temperatures and adequate sunlight are ideal.
Soil Nutrient Levels and Plant Health
The availability of essential nutrients in the soil significantly affects the overall health and development of peony plants. Soil testing can determine nutrient deficiencies, allowing for appropriate fertilization to promote robust growth and flowering.
FAQ Summary
How long does it take for peony seeds to germinate?
Germination time varies depending on the variety and stratification methods, but it can take anywhere from several weeks to several months.
Can I use any type of soil for planting peony seeds?
Peonies prefer well-drained, slightly acidic soil rich in organic matter. Avoid heavy clay soils.
What are the signs of a healthy peony seedling?
Healthy seedlings exhibit strong, vibrant green leaves, robust stems, and consistent growth.
How often should I fertilize my peony seedlings?
Fertilize sparingly, using a balanced, slow-release fertilizer once or twice during the growing season.
When is the best time to transplant peony seedlings?
Transplant in the fall or early spring after the danger of frost has passed.





















